AG — Prof. Heiko Rieger — Statistical Physics
Thiol dependent intramolecular locking of Orai1 channels
Dalia Alansary, Barbara Schmidt, Katrin Dörr, Ivan Bogeski, Heiko Rieger, Achim Kless & Barbara A. Niemeyer
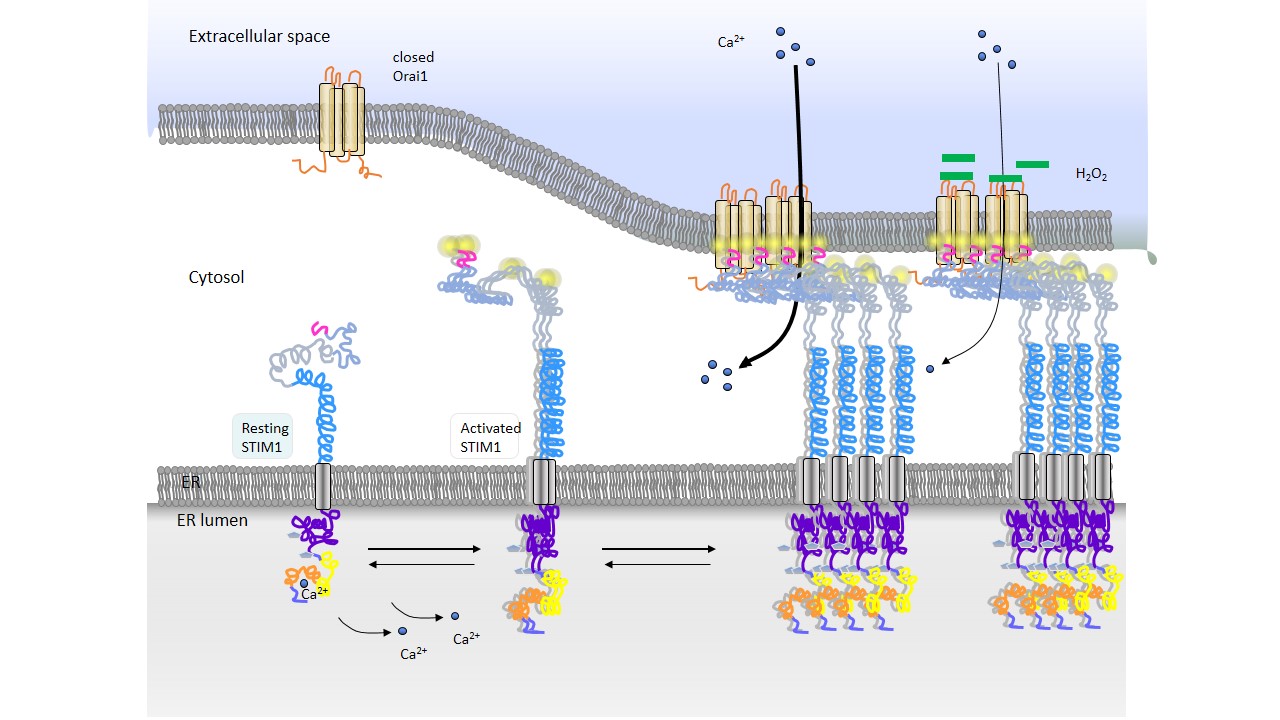
Differential Calcium Ca2+ signals drive alternate cell fates such as proliferation, apoptosis or tolerance. In immune cells one major entry pathway for Ca2+ into the cells are store-operated Ca2+ channels. In response to store depletion ER-resident Ca2+ sensor molecules STIM translocate to regions near the plasma membrane and interact with Orai1 proteins. These form the major ion conduction units mediating the Ca2+ release activated ICRAC (CRAC) current. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) interacting with cysteine residues can alter protein function. Pretreatment of Orai1 with the oxidant H2O2 reduces ICRAC . Our results demonstrate a novel mechanistic model for ROS-mediated inhibition of Orai1 and identify a candidate residue for pharmaceutical intervention.
Preincubation with ROS prevents activation of Orai1, but is unable to inhibit the channel complex once it is activatied [1]. The inhibition is mainly mediated through the reactive cysteine C195 at the exit of transmembrane region 3 of Orai1, a residue that is not conserved in the paralouge Orai3, which currents are not inhibited. We combine experimental and theoretical approaches and show that oxidation of Orai1 leads to reduced subunit interaction, slow diffusion and that either oxidized C195 or its oxidomimetic mutaion C195D virtually eliminates channel activation by intramolecular interaction with S239.
To assess whether the observed effects are sufficient to explain the dramatic oxidant inhibition of Orai1 mediated currents, we implemented the altered diffusion and reaction rates into a modified version of the stochastic reaction diffusion model that we have previously reported [2,3]. In addition, the model was modified to introduce and account for the locked channel subunits. With this the model also allows us to predict different degrees of inhibition depending on the fraction of inhibited channels.
References
| Mutations of the Ca2+-sensing Stromal Interaction Molecule STIM1 regulate Ca2+ influx by altered oligomerization of STIM1 and by destabilization of the Ca2+ channel Orai1 |
|
| J. Biol. Chem. 288, 1653 (2013) | [pdf] |
| Interplay of channels, pumps and organelle location in calcium microdomain formation |
|
| New J. Physics 15, 055022 (2013) | [pdf], [link] |
| Thiol dependent intramolecular locking of Orai1 channels |
|
| Sci. Rep. 6, 33347 (2016) | [pdf] |
Related link:scientific_reports_6_33347_(2016)
Legal notice (Impressum) Privacy policy



